The Banking Codes and Standards Board of India (BCSBI) was established in February 2006 as an independent and autonomous body registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
It was formed based on the recommendations of the Committee on Procedures and Performance Audit of Public Services chaired by Shri S.S. Tarapore (former Deputy Governor of RBI). The objective was to ensure fair treatment to customers by developing and monitoring adherence to banking codes and standards.
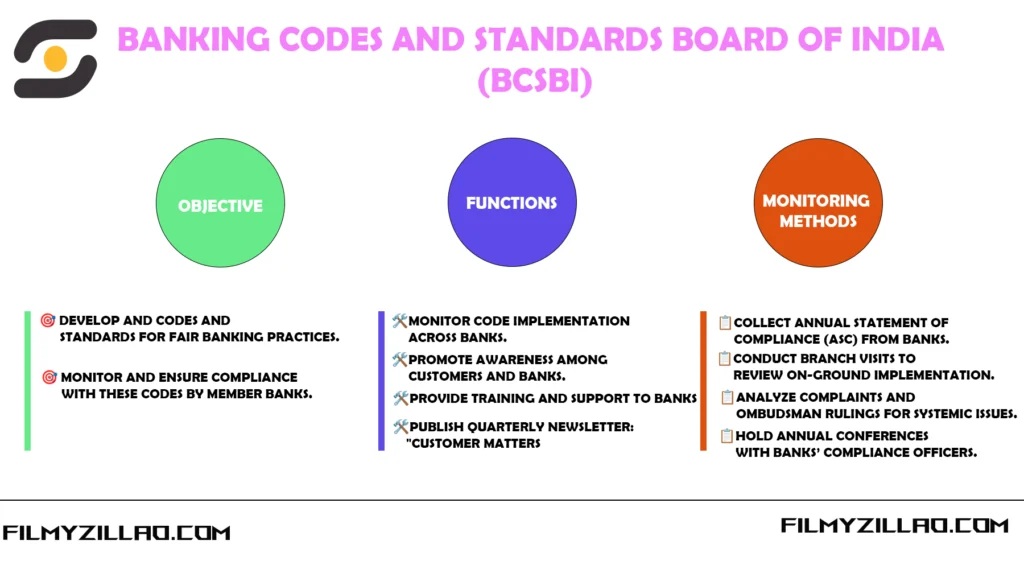
Objectives of BCSBI
- To plan, evolve, develop, promote, and publish comprehensive Codes and Standards for banks to ensure fair treatment of customers.
- To function independently and ensure adherence to the Codes and Standards by banks while delivering services.
Functions of BCSBI
- In collaboration with Indian Banks’ Association (IBA), BCSBI developed two main codes:
- Code of Bank’s Commitment to Customers
- Code of Bank’s Commitment to Micro and Small Enterprises
- These codes set minimum service standards that banks must follow while dealing with individual customers and MSEs.
- Monitor code implementation through:
- Annual Statement of Compliance (ASC) from member banks
- Branch visits
- Analysis of complaints and Banking Ombudsman rulings
- Annual conferences with compliance officers
Importance of BCSBI
- Ensured transparency in banking operations
- Promoted responsible banking practices
- Helped build customer trust and awareness
- Served as a guide for what customers could expect from their banks
- Conducted awareness campaigns and training for banks and customers
- Published a quarterly newsletter titled ‘Customer Matters’
Limitation
- BCSBI was not a grievance redressal forum. However, it analyzed systemic issues based on complaints and worked with banks to improve procedures.
Dissolution of BCSBI
It is important to note that BCSBI ceased operations and was dissolved in September 2021. The decision was made by its member banks and the Reserve Bank of India. While BCSBI no longer functions, its legacy lives on in the banking codes it helped develop.
Currently, the Reserve Bank of India and the Banking Ombudsman Scheme continue to ensure customer protection and fair banking practices.
Conclusion
BCSBI played a significant role in shaping responsible banking conduct in India. Though it has been dissolved, the standards and awareness it helped establish continue to influence the Indian banking sector today through regulatory mechanisms led by the RBI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is BCSBI?
BCSBI stands for Banking Codes and Standards Board of India. It was an independent body set up in 2006 to develop codes and standards for fair treatment of customers by banks in India.
2. Who set up BCSBI and why?
BCSBI was set up based on the recommendations of the Committee on Procedures and Performance Audit of Public Services, chaired by Shri S.S. Tarapore. The goal was to ensure transparent, fair, and customer-friendly banking services.
3. Is membership to BCSBI mandatory for banks?
No, membership of BCSBI was voluntary. However, most scheduled commercial banks and some cooperative and regional rural banks were members.
4. What were the main codes developed by BCSBI?
BCSBI developed two major codes:
- Code of Bank’s Commitment to Customers
- Code of Bank’s Commitment to Micro and Small Enterprises
These codes set minimum standards of banking services and practices.
5. What role did BCSBI play in customer grievance redressal?
BCSBI was not a grievance redressal forum. It did not handle individual complaints but would analyze them to identify systemic issues and recommend changes to prevent future occurrences.
6. Is BCSBI still active?
No, the BCSBI was officially dissolved in September 2021. Its functions and objectives have now been integrated into the Reserve Bank of India’s broader framework for consumer protection.
7. Where can customers go for banking complaints now?
Customers can approach the Banking Ombudsman, RBI’s Consumer Education and Protection Department, or use the RBI CMS portal (https://cms.rhttps://cms.rbi.org.inbi.org.in) for grievance redressal.