The Enhanced Access and Service Excellence (EASE) Reforms represent a major transformation initiative by the Government of India to revitalize Public Sector Banks (PSBs). These reforms are aimed at enhancing performance, governance, and customer-centric service delivery across India’s public banking sector.
Background & Genesis of EASE Reforms
The journey began with the “Gyan Sangam” (Knowledge Confluence) held in Pune in January 2015, where top executives of PSBs and financial institutions engaged in deep discussions on the challenges faced by the banking sector. This event identified urgent needs in improving financial stability, NPA resolution, credit growth, risk management, and technological adoption. It laid the intellectual foundation for a structured reform agenda.
Further momentum was provided by the ‘PSB Manthan’ conference held in Gurugram in November 2017, where over 250 Whole-Time Directors and senior executives from PSBs came together. Their discussions culminated in a unified roadmap—the EASE agenda—which was officially launched as EASE 1.0 on 24 January 2018, with 30 action points across 6 core themes.
The 4R’s Strategy: Foundation of PSB Reforms
To tackle deep-rooted issues in PSBs, the Government launched a comprehensive 4R’s strategy in 2015:
- Recognition: Transparent identification of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs).
- Resolution: Ensuring timely resolution and recovery of stressed assets.
- Recapitalization: Strengthening bank balance sheets with capital infusion.
- Reforms: Structural and institutional reforms in governance, risk management, lending practices, and technology integration.
The first three R’s focused on cleansing balance sheets, while Reforms aimed at systemic change, ensuring that problems like NPAs do not recur.
EASE: A Structured Reform Journey
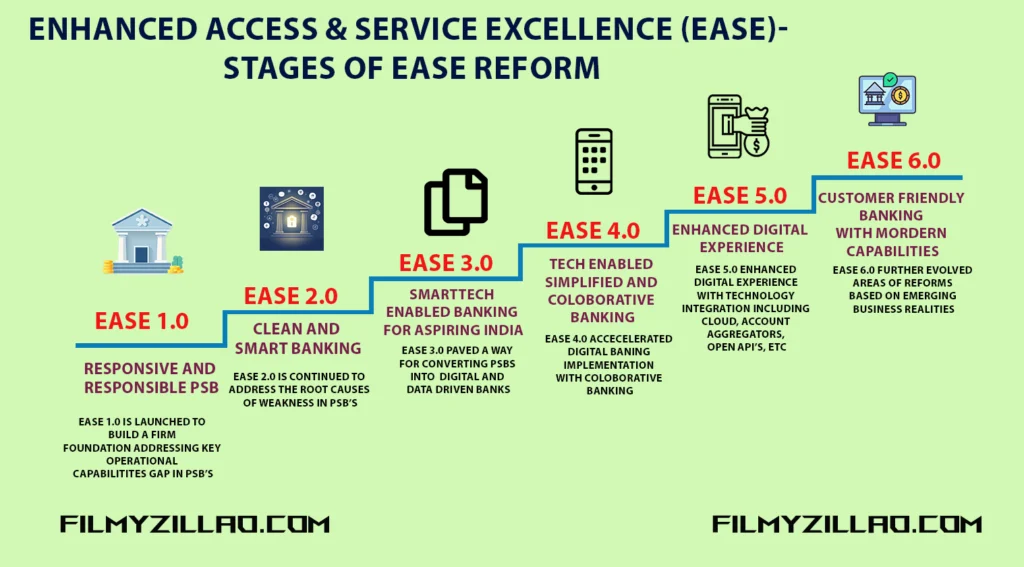
The EASE reforms evolved in phases, each version building upon the learnings of its predecessor. These reforms cover areas like prudential lending, risk management, technology-enabled controls, customer service excellence, and transparent governance.
EASE 7.0: A Vision for 2024 and Beyond
EASE 7.0 expands the reform scope under five strategic pillars:
Key 1: Banking Towards ‘Viksit Bharat’
- Expand MSME customer base via digital tools.
- Identify and build deep expertise in focus economic sectors.
- Promote women entrepreneurship through inclusive banking.
- Accelerate CASA growth via tailored products.
- Deepen youth engagement in banking services.
- Push agricultural lending beyond traditional models like KCC.
- Develop climate-resilient lending practices and risk frameworks.
Key 2: Excellence in Customer Service
- Enhance customer experience across digital and branch interfaces.
- Strengthen long-term customer relationships.
- Improve process efficiency to ensure ease and convenience.
Key 3: Adoption of New-age Technology
- Initiate GenAI use-case pilots.
- Boost data governance and advanced analytics.
- Implement digital operating models for cost and quality optimization.
- Adopt cloud infrastructure for scalable data processing.
Key 4: Effective Risk/Fraud Management, Recovery
- Enhance operational and cyber risk resilience.
- Expedite NPA recovery through DRT/NCLT streamlining.
- Digitize collections for better tracking and efficiency.
- Improve credit and market risk monitoring.
Key 5: Developing Employees for Emerging Priorities
- Link employee productivity to measurable outcomes and diversity.
- Use data-driven HR strategies for workforce planning.
- Personalize employee development through tailored learning solutions.
EASE Reforms Index: Monitoring Progress
To ensure effective implementation, the EASE Reforms Index was created. It enables:
- Performance tracking within and across PSBs.
- Transparent benchmarking and reform prioritization.
- PSBs to create custom indexes aligned with internal goals.
- Linkage of employee performance metrics to reform outcomes.
This accountability mechanism encourages banks to set up centralized teams to drive the reforms and align employee incentives with transformation milestones.
Conclusion
The EASE banking reforms signify a bold and strategic shift towards making Public Sector Banks future-ready. By combining policy reforms, technology integration, customer-first strategies, and strong governance, the Government of India is empowering PSBs to become pillars of economic growth and financial inclusion in a ‘Viksit Bharat’ (Developed India). Through EASE 7.0 and beyond, PSBs are being equipped to not only serve the current needs but to anticipate and lead the future of banking in India.