Last updated on December 25th, 2024 at 03:56 pm
Businesses in India are categorized into Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) based on two key factors: investment in plant and machinery and annual turnover. This classification plays a vital role in defining the economic backbone of the country.
The MSME sector contributes significantly to the Indian economy, accounting for:
- 29% of the GDP
- Nearly one-third of manufacturing output
- Approximately 49% of the country’s exports
By driving uniform growth across sectors and regions, MSMEs foster a more stable economy.
In this article, we’ll explore the basics of MSME and their classification.
What Does MSME Stand For?
MSME stands for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises. These businesses form the foundation of India’s economic development, each categorized based on defined thresholds of investment and turnover.
The concept of MSMEs was first introduced through the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, which has since been refined by the government to better suit the evolving economy.
The MSMED Act, 2006
The MSMED Act, 2006 was established to:
- Promote, develop, and enhance the competitiveness of MSMEs.
- Enable MSME entrepreneurs to improve efficiency, expand their activities, and thrive in competitive markets.
- Provide clear criteria for the classification of MSMEs.
This Act also formalized the process of Udyam Registration, a mandatory online registration for MSMEs to access government benefits.
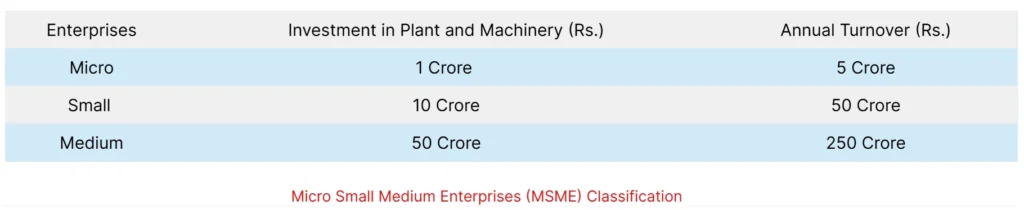
MSME Classification
Under the revised MSME classification system, businesses are categorized based on investment in plant and machinery or equipment and annual turnover.
1. Micro Enterprises
- Investment: Up to ₹1 crore
- Turnover: Up to ₹5 crore
2. Small Enterprises
- Investment: Up to ₹10 crore
- Turnover: Up to ₹50 crore
3. Medium Enterprises
- Investment: Up to ₹50 crore
- Turnover: Up to ₹250 crore
Note: MSMEs must engage in activities such as the manufacturing or production of goods (as per the Industries Development & Regulation Act, 1951) or in providing services.
Challenges Faced by the MSME Sector
Despite its significance, the MSME sector in India faces several challenges:
- Infrastructural bottlenecks
- Limited access to credit and capital
- Policy and institutional gaps
- Difficulty in formalizing operations
- Limited market linkages and public procurement opportunities
- Need for capacity building
- Technological advancements for operational improvement
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the sustainable growth of the MSME sector.
Government Initiatives to Support MSMEs
To strengthen the MSME ecosystem, the Government of India has implemented various schemes, including:
1. Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
Encourages self-employment by providing financial support.
2. Udyam Registration
Simplifies the registration process for MSMEs, making them eligible for government benefits.
3. Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
Offers credit guarantees to facilitate easier access to loans.
4. Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS)
Provides financial assistance during unforeseen challenges, such as economic disruptions.
5. Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency Ltd (MUDRA)
To provide financial assistance to the small business owners.
Conclusion
The MSME sector is a vital driver of India’s economic growth, fostering innovation, employment, and equitable development. With supportive policies and government initiatives, MSMEs continue to thrive and contribute significantly to the nation’s progress.
For a developing country like India, a robust MSME sector ensures a healthy economy and a brighter future.
Pingback: CGTMSE Guarantee Cover for MSMEs: Eligibility, Benefits, and How to Apply - Fil Zill
Pingback: TReDS Platform- Trade Receivables Discounting System - Fil Zill